What is a Web search engine?
A customized computer server that searches the Web for information is a Web search engine. A user query’s search results are frequently presented as a list (sometimes called hits). The hits could include web pages, pictures, and other file kinds. Some search engines also look for and return information from open directories or public databases. Human editors update online directories, but search engines function algorithmically or with a combination of algorithmic and human input. This is how search engines vary from web directories.
Large-scale data mining applications are essentially what web search engines are. All aspects of search engines use various data mining techniques, including crawling (5, for example, deciding which pages should be crawled and the crawling frequencies), indexing (6, for example, determining which pages should be indexed and how much the index should be built), and searching (7, for example, deciding how pages should be ranked, which advertisements should be added, and how the search results can be personalized or made “context-aware”).
Data mining faces significant obstacles from search engines. They have a massive and constantly expanding amount of data to manage first. Such data typically cannot be processed by only one or a few devices. As a substitute, search engines frequently need to use computer clouds, tens of thousands or even hundreds of thousands of computers that work together to mine enormous amounts of data. There is still room for research in scaling out data mining techniques over computer clouds and sizable distributed data sets.
How do search engines work?
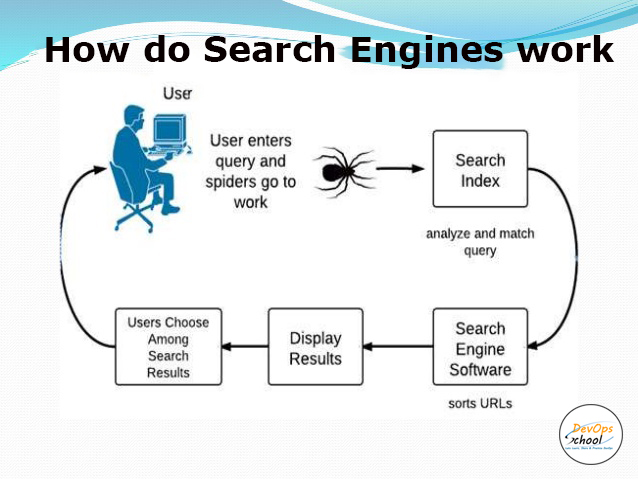
- Search the Internet for content while crawling, examining each URL’s code and content.
- Indexing: Arrange and store the information gathered throughout the crawling process. Once a page is indexed, it has a chance of being returned as a response to pertinent searches.
- Results are ranked from most relevant to least relevant to deliver the content that best satisfies a searcher’s inquiry.
Crawling:
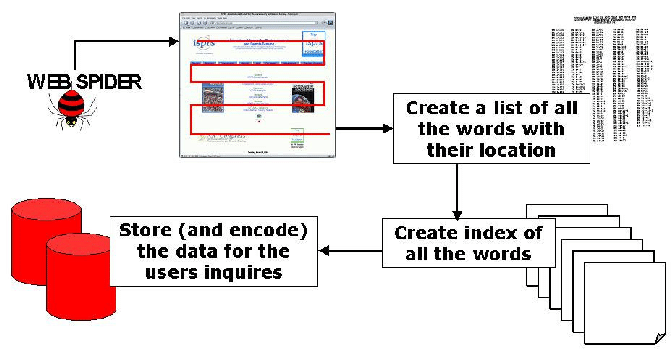
Crawling is the first step in the actual process of finding new websites online.
Web crawlers, sometimes known as bots or spiderbots, are tiny programs used by search engines to track links from well-known pages to newly discovered ones.
When a web crawler accesses a new webpage via a link, it reads the page’s content, passes it along for additional processing (a process known as indexing), and then resumes its search for other webpages.
Indexing:
The process of verifying and saving the content from the webpages in the search engine’s database, known as the “index,” begins once the bots have finished crawling the data. Essentially, it is a vast library of all the websites.
It must first be indexed for your website to appear on the search engine results page. Remember that indexing and crawling are ongoing procedures that repeatedly occur to keep the database current.
The webpage can be utilized as a search result for a possible query after it has been examined and saved in the index.
Ranking:
The final stage consists of selecting the top outcomes and compiling a list of pages that will show up on the result page.
Each search engine uses numerous ranking signals, most of which are kept private and not accessible to the general public.
Directory search engines:
Some specialized search engines function as content directories. This indicates that they only display results for personally added content. They do not crawl the Internet. SEO strategies can still be applied to dominate these directory search engines for pertinent queries. See several search engine kinds.
What happens when a search is performed?
When a user enters a search query into a search engine, all of the sites that are considered relevant are pulled from the index and ranked in a set of results using a hierarchical algorithm.
Each search engine uses different algorithms to determine the most pertinent results. For instance, a page that performs well for a search query on Google might not do well on Bing.
Search engines use other pertinent information in addition to the search query to produce results, such as:
- Location – Some search terms, like “cafes near me” or “movie times,” depending on your geographic location.
- Language detection – If the user’s language can be identified, search engines will return results in that language.
- Previous search history – Depending on what a user has previously searched, search engines will return different results for a query.
- Device – A different set of results can be given depending on the device from which the question was done.
How do search engines make money?
Search engine results come in two varieties:
- Natural outcomes from the search index. You can’t buy your way in here.
- Advertisements’ compensated outcomes. To be here, you can pay.
The advertiser compensates the search engine every time someone clicks on a paid search result. Pay-per-click (PPC) advertising is what this is.
Due to this, market share is essential—a higher user base results in more ad clicks and money.
Why should you care how search engines work?
You may rank your website in organic search results for relevant and well-liked terms by understanding how search engines find, index, and rank content.
Your article will receive more visits and organic traffic if you can rank highly for these keywords.
What is a search engine algorithm?
The term “search engine algorithm” refers to a sophisticated network of numerous algorithms that examines all of the indexed pages and chooses which ones should show up in the search results for a particular query.
For instance, the Google algorithm takes into account hundreds of variables (many of which are well-known, while others are kept a secret) in a variety of fields, including:
- The query’s intent (understanding what the user means by using the exact words they used, what is the search intent, etc.)
- Website relevance (the search engine needs to find out whether the page answers the search query)
- Content excellence (the algorithms determine whether the webpages are an excellent source of information based on internal and external factors; the number and quality of backlinks are important factors here)
- Website usability (considers the quality of the webpage from the technical standpoint – responsiveness, page speed, security, etc.)
Search engine optimization:
Search engines not only give their consumers vital information, but they may also aid businesses in promoting their websites. Any internet marketing strategy should include optimizing your website for relevant search terms because it can increase traffic to your web pages. Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the collective term for website owners’ actions to raise their search ranks (SEO).
If we wanted to condense SEO, we could say that the three most crucial elements are:
- Technical Optimization
- Great content
- Quality backlinks
FAQ,s:
What was the first search engine?
In 1990, a student named Alan Emtage developed the first search engine, called Archie (after the word “Archives”).
Although other indexing tools (like “X.500” or “Whois”) existed earlier, Archie was the first accurate search engine that could locate specific files online.
Archie had a reasonably straightforward operation: it browsed the websites accessible via the Internet and listed them as downloadable files. The result pages were a plain list because they could not index the websites’ content.
What is the difference between a browser and a search engine?
A web browser software program (such as Chrome, Firefox, Microsoft Edge, etc.) is installed on a computer or mobile device. The browser’s job is to display web pages with an intuitive user interface.
A search engine is an internet tool that may be used by a web browser, such as Google, Bing, Yahoo!, etc. A search engine’s primary function is to deliver relevant web pages from user queries.
What are examples of Web search engines?
List of the top 12 search engines worldwide
- Google. The best search engine in the world is the Google Search Engine, which is also one of Google’s most well-liked products.
- Bing. Bing, Microsoft’s response to Google, was introduced in 2009.
- Yahoo
- Baidu
- ALL
- Ask.com
- Excite
- DuckDuckGo.