“illiteracy” refers to a person’s inability to read or write clearly, severely restricting their capacity to learn and communicate knowledge through written language. Illiteracy is a significant problem worldwide, affecting both developed and developing nations to varied degrees. There are many harmful social, economic, and individual effects of Illiteracy. We shall examine the benefits and drawbacks of Illiteracy in this debate and some of its salient characteristics.
What is Illiteracy?
Illiteracy, the inability to read and write well, has far-reaching implications that affect individuals, communities, and entire societies. It is a problem that still exists in many places, impeding individual growth and economic advancement. We shall examine ten significant effects of Illiteracy in this essay.
Features of Illiteracy:
- Numerous Variations
- Inter-generational Cycle
- Gender Inequalities
- Urban and rural disparities
- Initiatives Intended to Combat Illiteracy
Disadvantages of Illiteracy:
- Limited Access to Information: Illiterate People need more access to written information, which can make it difficult for them to make well-informed decisions about their health, education, and finances, among other areas of their lives.
- Reduced Employment Opportunities: Lack of literacy can significantly reduce one’s ability to get employment and make money. Many vocations require at least fundamental reading and writing abilities, and those who lack these abilities may only be able to work in low-paying labor-intensive jobs.
- Lower Educational Attainment: Illiteracy frequently results in lower levels of education, which keeps people in a cycle of limited options and socioeconomic disadvantage for themselves and their communities.
- Communication Barriers: People who lack literacy may find it challenging to communicate with others in a literate society, which can cause them to feel alone, misunderstood, or excluded.
- Vulnerability to Exploitation: Illiterate People are frequently more susceptible to being taken advantage of and duped because they may find it challenging to comprehend contracts, legal documents, or misleading marketing.
10 Consequences on Society of Illiteracy
1. Limited Educational Opportunities:
When we talk about limited educational chances, we mean that only some have the same access to high-quality education and educational resources, which is frequently a result of many socioeconomic, geographic, and cultural circumstances. Given the importance of education for individual growth, social mobility, economic prosperity, and general well-being, this topic has significant ramifications for people, communities, and nations. Here, we’ll look at limited educational options and its broad ramifications.
2. Economic Disparities:
Economic disparities are significant discrepancies in wealth, income, and access to economic opportunities across people, groups, or regions within a society. Different elements, such as historical, social, and economic contexts, can contribute to these discrepancies. Economic disparity significantly impacts both individuals and society, impacting things like social mobility, education, and health. In this section, we’ll examine the idea of economic inequality and its ramifications.
3. Poor Health Literacy:
Poor health literacy is the inability of a person to successfully obtain, comprehend, assess, and apply health information to make and promote decisions about their health and healthcare. There are significant public health implications for both people and society at large. Here, we’ll look at inadequate health literacy and its effects.
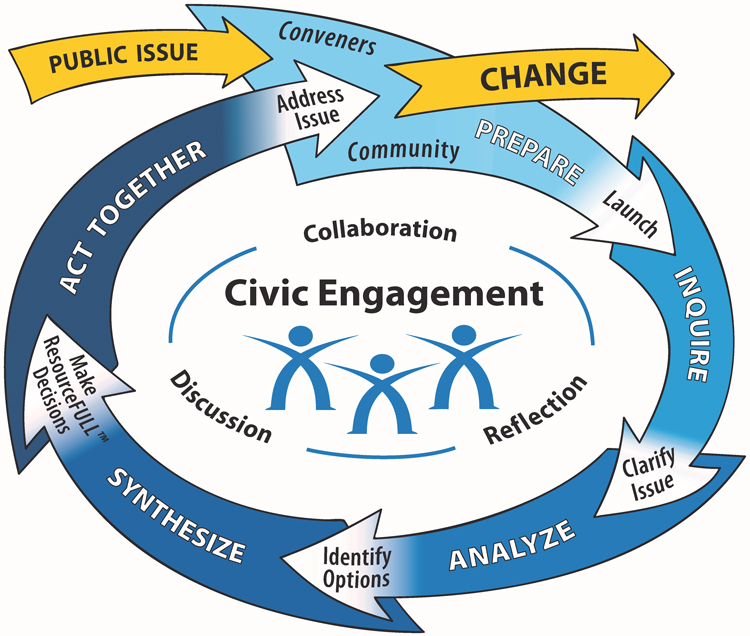
4. Reduced Civic Engagement:
Reduced civic engagement is the term used to describe a loss in people’s active engagement in their communities and the political systems that control their countries. A strong democracy depends on its citizens partaking in a wide range of activities, including voting, volunteering, community organizing, and engaging in public discourse. A democratic society’s functioning ability might suffer significantly when civic involvement falls off. Here, we’ll look at decreased civic engagement and its effects.
5. Social Isolation:
When socially isolated, people don’t have many other people to contact, connect with, or form relationships with. It frequently results in emotions of isolation, disconnection from others, and social isolation. The effects of social isolation on a person’s mental, emotional, and physical health and society can be profound. In this section, we’ll look at the idea of social isolation and its effects.
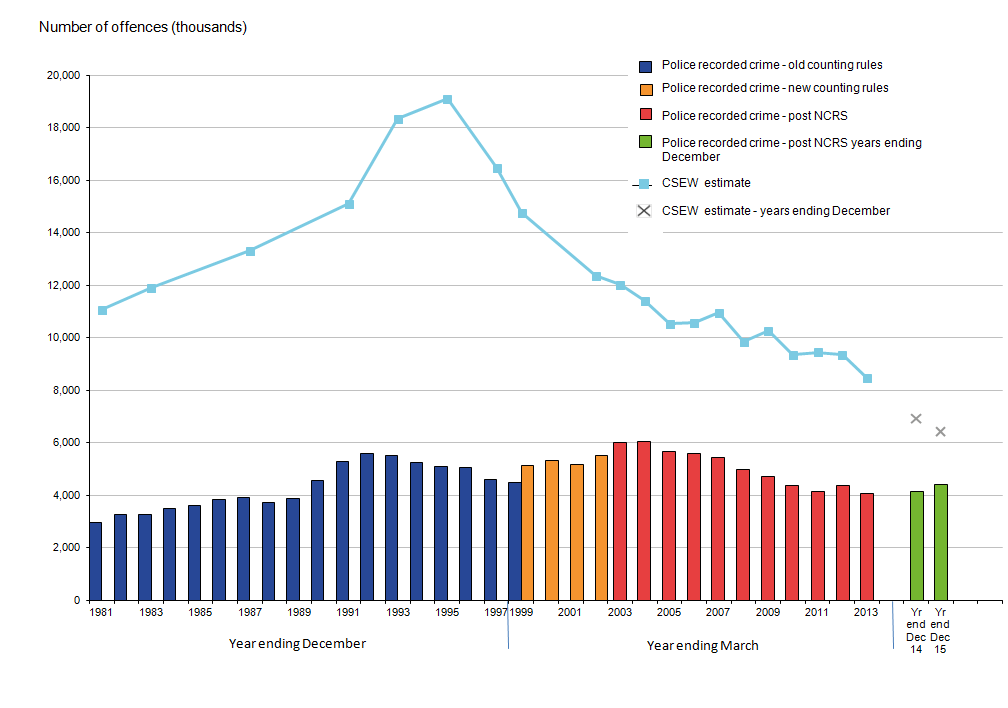
6. Increased Crime Rates:
A spike in criminal activity in a particular area or community increases crime rates. Theft and vandalism are examples of property crimes, as are assault and murder, as well as violent and white-collar offenses like fraud and embezzlement. When crime rates rise, it significantly affects everyone’s safety, the health of the neighborhood, and how well society functions. Here, we’ll examine several essential causes of rising crime rates and their effects.
7. Interferes with Family Well-being:
The term “interference with family well-being” refers to various elements and situations that may disrupt or adversely affect the stability and health of families. Families are the cornerstone of communities. Thus, family well-being is crucial for the general health of people and society. Following are some typical elements that may harm family harmony:
8. Global competitiveness:
The ability of a country to successfully compete in the international market is referred to as global competitiveness. It includes various elements and characteristics that affect a nation’s ability to draw foreign direct investment, spur economic expansion, and thrive in a globally interdependent society. In this section, we’ll examine the idea of global competitiveness and its importance.
9. Strain on Social Services:
The pressure and difficulties faced by government-run or -supported programs and services that aid people and communities in need are called “strain on social services.” Some examples include health care, education, welfare, housing, and other services. When these services are overburdened, it can have substantial short- and long-term effects on society. We shall discuss the strain on social services in this section, along with any repercussions.
10. Hindrance to Technological Advancement:
The term “hindrance to technological advancement” refers to the barriers, difficulties, or other elements that slow new technology’s rapid creation and uptake. These obstacles range from social and cultural opposition to legal and economic restrictions. Understanding the obstacles to technological development is essential since technology has significantly influenced how our modern world has developed. Here are some crucial elements of this problem.
Conclusion:
Illiteracy is a systemic problem with far-reaching repercussions, not just personal. It is crucial for both individual growth and the development of societies to address Illiteracy through better access to education, literacy initiatives, and a dedication to lifelong learning. We can work towards a more equal and prosperous future for everybody if we acknowledge and address the effects of Illiteracy.
FAQ:
What exactly is literacy?
An illiterate person needs help to read or write clearly, making it difficult to comprehend, interpret, and communicate using written language.
How is the literacy rate determined?
The percentage of illiterate people within a given population is often used to calculate the rate of Illiteracy.
What are the main reasons why people are illiterate?
The lack of access to high-quality education, poverty, cultural hurdles, and societal attitudes toward literacy are only a few causes of Illiteracy.
Is there a worldwide literacy problem?
Yes, there is a global problem with varied levels of Illiteracy in various nations and areas. Both developed and developing countries struggle with it.