As Python ecosystems become more automated, cloud-native, and AI-assisted, developers are increasingly encountering non-standard error identifiers instead of classic exceptions. One such case that continues to confuse developers in 2026 is Python 54axhg5.
Despite what many short articles suggest, Python 54axhg5 is not a built-in Python error. Treating it as one leads to wasted debugging time and incorrect fixes. This guide explains what 54axhg5 actually represents, why it exists, and how modern Python systems generate it, with practical debugging strategies used by professionals in 2026.
What Is Python 54axhg5?
Python 54axhg5 is an internal error reference code, not a Python exception class.
Python itself does not define:
-
Error 54axhg5 -
Exception 54axhg5 -
Any numeric–alphanumeric error format like this
Instead, 54axhg5 is typically generated outside Python, then surfaced inside Python logs or outputs.
What makes it confusing?
Because it appears during Python execution, developers assume:
-
Python caused it
-
It belongs to the Python standard library
-
It has a universal fix
None of these are true.
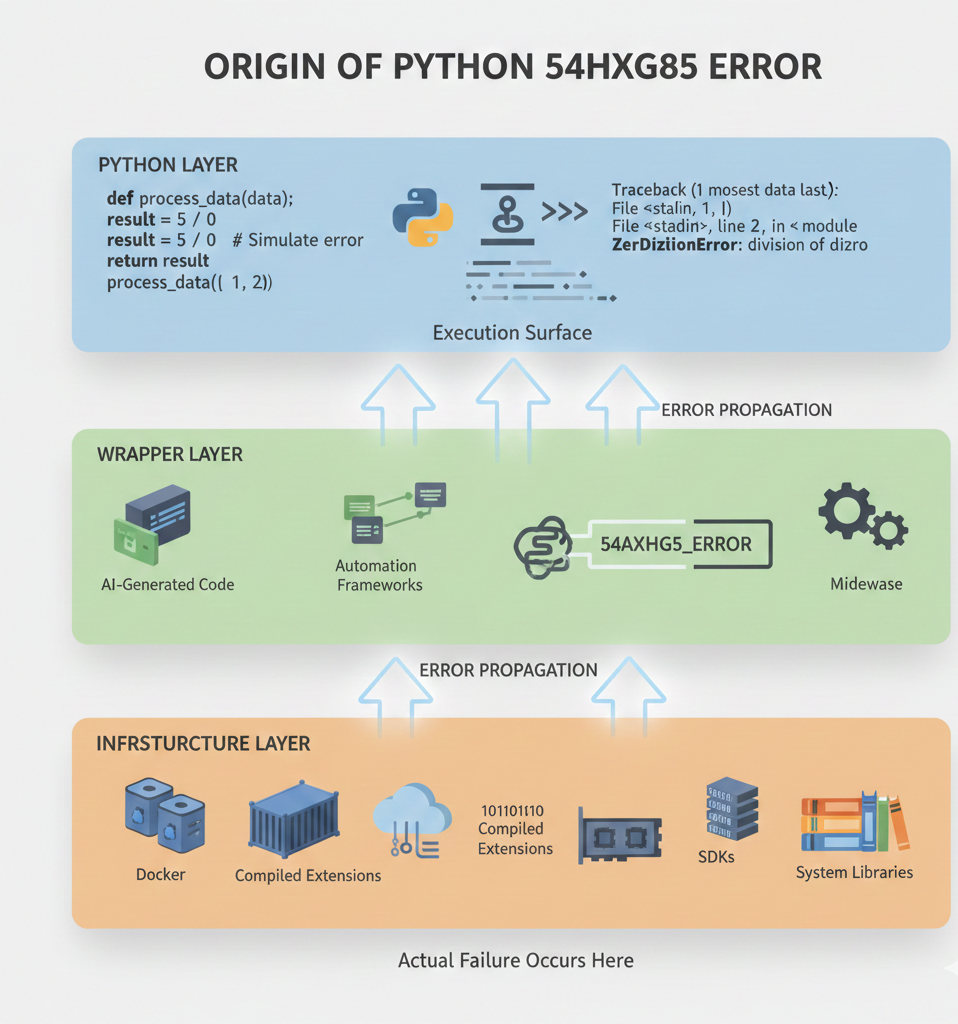
Why Python 54axhg5 Exists (Explained Simply)
In modern systems, Python often acts as an execution layer, not the root controller.
When an underlying system fails, it may:
-
Generate an internal error ID (e.g.,
54axhg5) -
Pass only that ID upward
-
Suppress the original low-level error for security or abstraction
Python then logs or displays the ID instead of the cause.
Why Python 54axhg5 Errors Are More Common in 2026
Several 2026 development trends explain the rise of identifier-style errors.
1. AI-Generated and Agent-Based Code
Python projects increasingly rely on:
-
Autonomous coding agents
-
AI-generated scripts
-
Dynamic runtime logic
These systems use hash-style identifiers to track failures across multiple execution paths.
2. Serverless and Ephemeral Runtimes
In AWS Lambda, Cloudflare Workers, and containerized platforms:
-
Full stack traces are often stripped
-
Only a reference ID (like 54axhg5) is preserved
3. Compiled Python Extensions
Many Python libraries rely on native code (C/C++, CUDA, Rust):
-
Errors occur outside Python’s exception system
-
Only an internal identifier reaches Python
Common Situations Where Python 54axhg5 Appears
Based on real-world debugging patterns, Python 54axhg5 most often shows up in:
▸ AI & Machine Learning Pipelines
-
Model loading failures
-
GPU/CPU device mismatches
-
Corrupted model artifacts
▸ Cloud-Based Python Applications
-
Serverless functions
-
Auto-scaling microservices
-
Short-lived containers
▸ Automated or Scheduled Scripts
-
Cron jobs
-
CI/CD pipelines
-
Headless background tasks
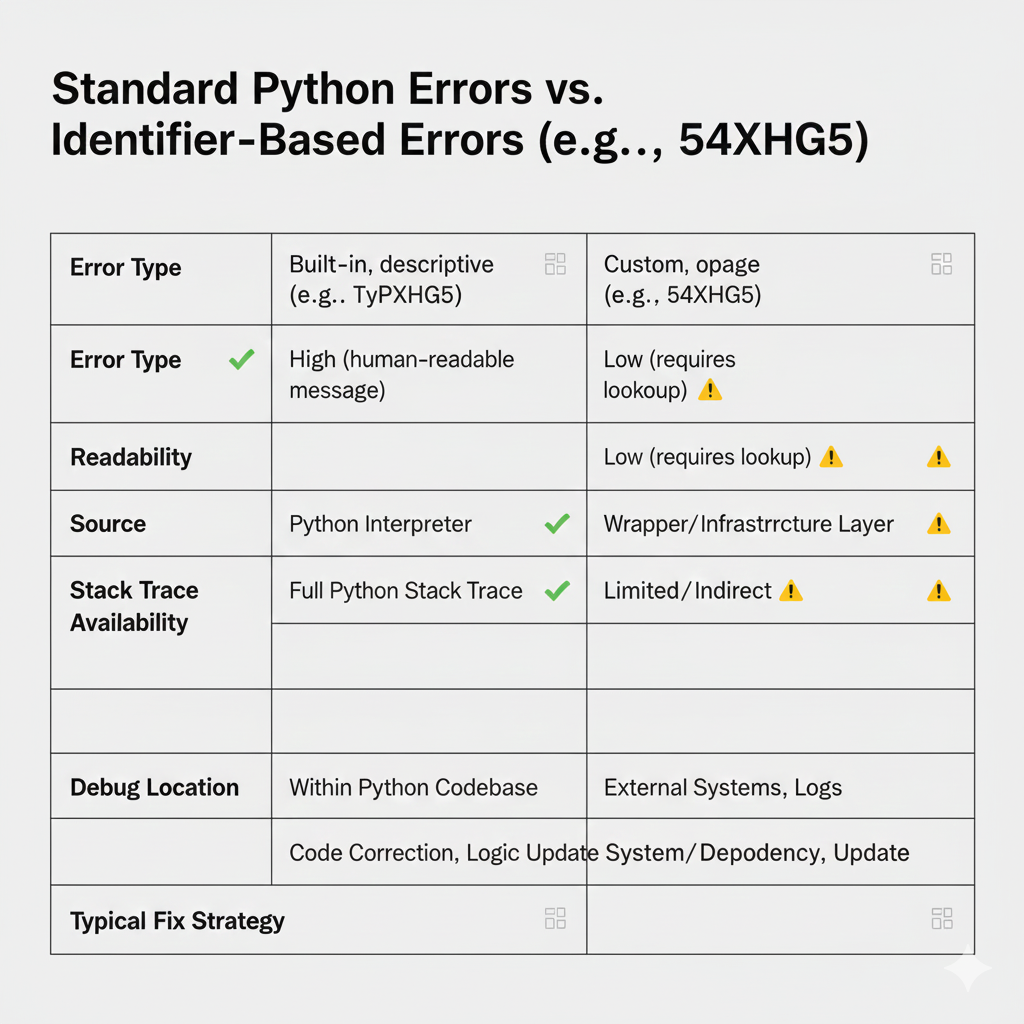
Python 54axhg5 Is NOT a Syntax or Runtime Error
This distinction is critical.
Error Type |
Is 54axhg5? |
|---|---|
SyntaxError |
❌ No |
TypeError |
❌ No |
ImportError |
❌ No |
Application-layer reference |
✅ Yes |
Infrastructure-level signal |
✅ Yes |
Trying to “fix” it with Python syntax changes usually fails, because the issue lives elsewhere.
Root Causes Behind Python 54axhg5 (2026 Analysis)
1. Dependency Version Mismatch
In 2026, Python dependency trees are deeper than ever.
Common trigger:
-
Library compiled against a different Python version
-
Silent binary incompatibility
Why it surfaces as 54axhg5:
-
The native layer fails
-
Python only receives the failure ID
2. Environment Drift
A script works locally but fails in production.
Typical causes:
-
Different OS architecture
-
Missing system libraries
-
Container image mismatch
The runtime hides sensitive details and returns 54axhg5 as a safe reference.
3. AI or Automation Layer Failures
Auto-generated code often includes:
-
Runtime guards
-
Internal failure keys
-
Obfuscated error handling
When something breaks, 54axhg5 becomes the tracking handle, not the explanation.
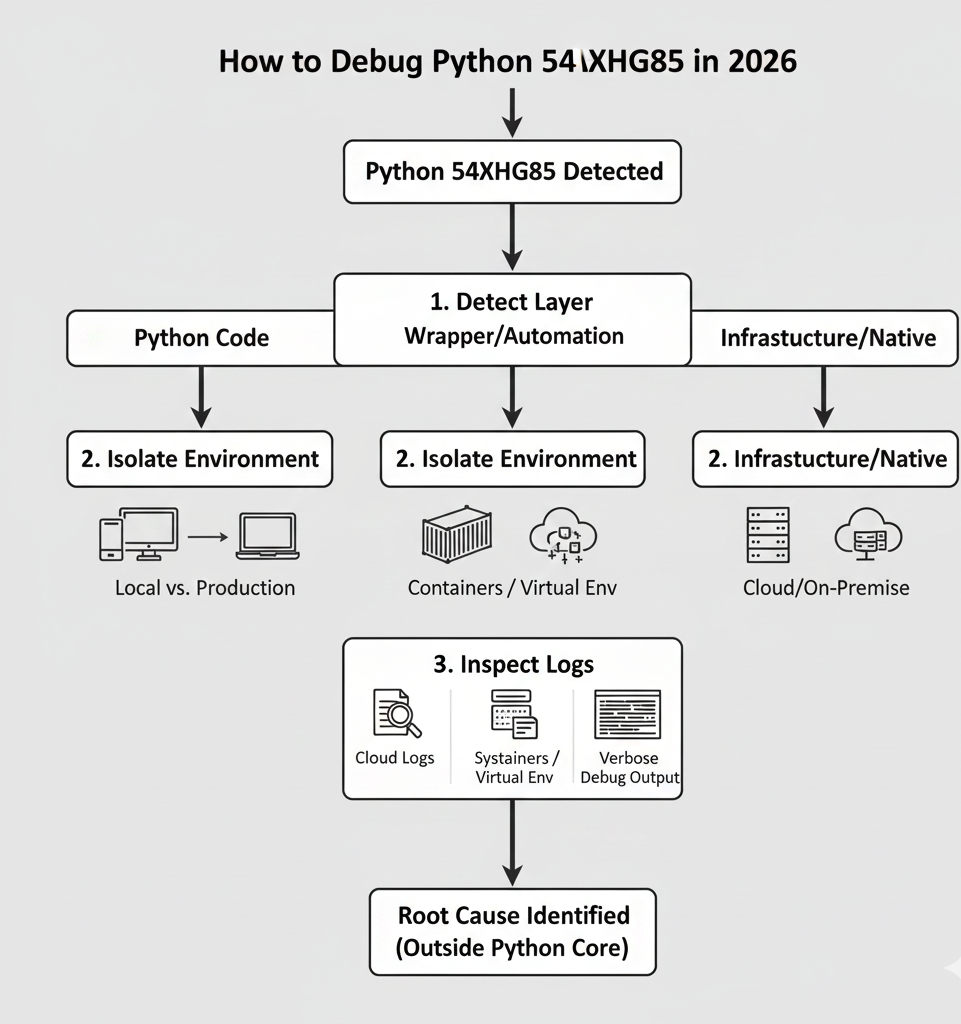
How Professionals Debug Python 54axhg5 in 2026
Step 1: Enable Verbose Logging
Always re-run with maximum verbosity:
-
Debug flags
-
Full stack tracing
-
Underlying service logs
In many cases, the real error appears one layer below Python.
Step 2: Trace the Execution Boundary
Ask:
-
Where does Python hand control to another system?
-
Is this calling native code, an API, or a service?
The answer usually leads directly to the cause.
Step 3: Reproduce Outside Automation
Run the same logic:
-
Without AI-generated wrappers
-
Without orchestration layers
-
In a minimal Python environment
If the error disappears, the wrapper not Python is responsible.
Python 54axhg5 vs Standard Python Errors
How to Prevent Python 54axhg5 Errors (Best Practices 2026)
✔ Pin Dependencies Strictly
Use lock files and reproducible builds to avoid binary drift.
✔ Avoid Silent Error Wrappers
If you control the system, force:
-
Explicit exceptions
-
Error message propagation
✔ Monitor Infrastructure Logs
In 2026, the real answer is often in cloud logs, not Python output.
People Also Ask (Answered Clearly)
Is Python 54axhg5 a virus or malware?
No. It is an internal reference code, not malicious software.
Can I fix Python 54axhg5 by reinstalling Python?
Rarely. Python itself is almost never the cause.
Does Python 54axhg5 mean my code is broken?
Not necessarily. It often means an external dependency failed.
Why do I only see this error in production?
Because production systems often suppress internal error details for security reasons.
Final Expert Take (2026 Perspective)
Python 54axhg5 is not a mystery bug, it’s a symptom of modern software complexity.
As Python continues to power:
-
AI systems
-
Cloud platforms
-
Automated pipelines
Developers must shift mindset from:
“What’s wrong with Python?”
to:
“Which layer failed before Python could explain it?”
Understanding that distinction is what separates frustrated debugging from professional-level diagnosis in 2026.