What is a Ransomware Attack?
The fundamental tenet of a classic ransomware assault is that businesses will pay a ransom in return for the secure decryption and restoration of their encrypted data. Companies will pay the ransom to work the network again and reduce downtime.
However, security teams have attempted to lessen the effect that data loss has on their companies as ransomware assaults have increased in frequency. Standard ransom-for-data assaults are no longer as effective because of safeguards such as secure off-site backups and segmenting significant network portions.
How to Prevent Ransomware:
A thorough ransomware resilience plan that considers readiness, prevention, and reaction in the event of an attack are essential. Here are a few ransomware prevention strategies for double/triple extortion assaults that you can use.
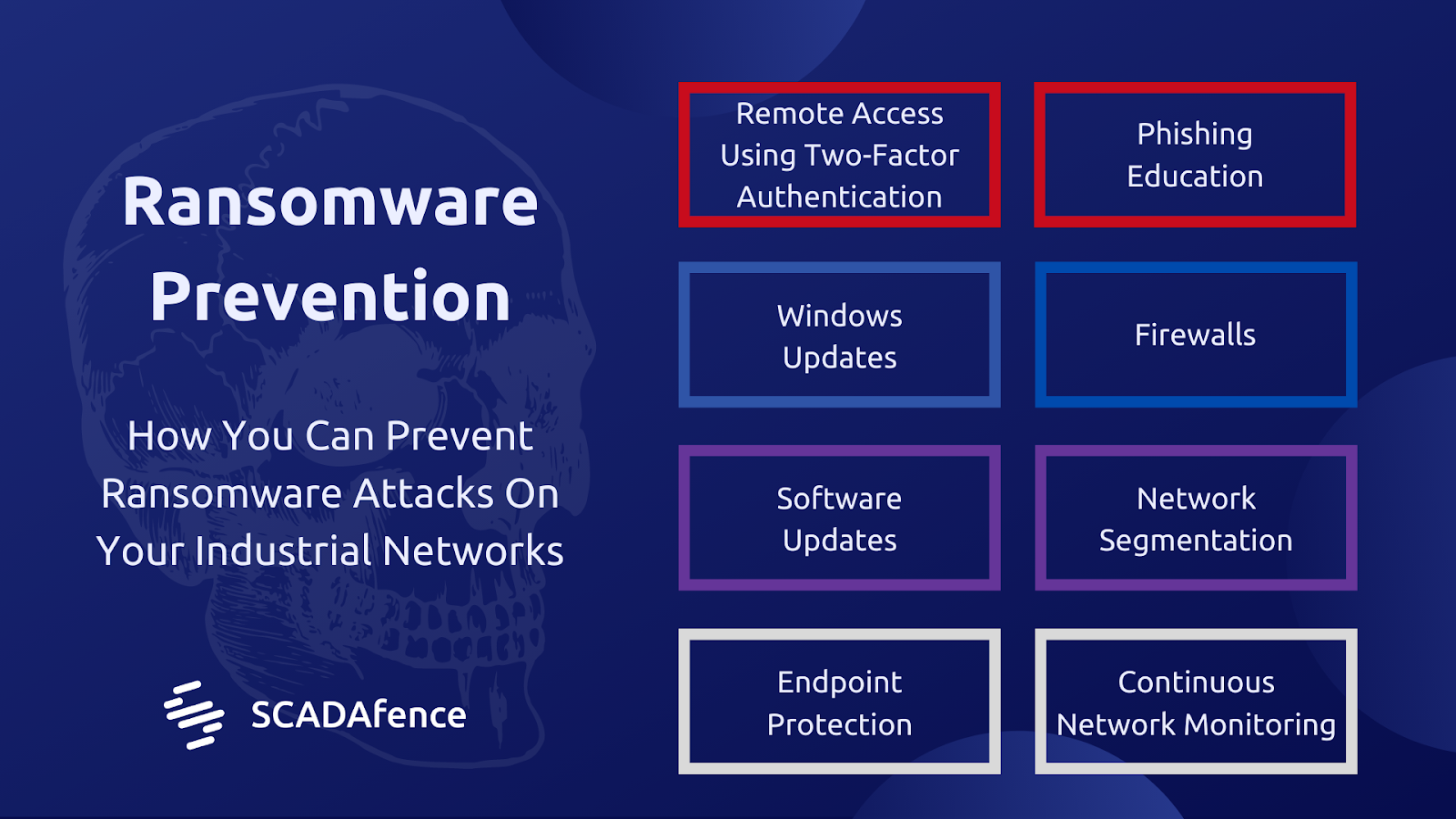
Don’t Let Attackers In Double extortion ransomware attacks enter your network using the same techniques as regular ransomware attacks. Protecting RDP ports and VPNs, password rules, multi-factor authentication, routine patching of known vulnerabilities, and security awareness training for staff are required to prevent initial access. You can also think about spending money on ransomware detection and web application firewall.
Backups and Data Encryption: A recent offline backup can shield you from the first stage of a ransomware assault, which is the recovery of your data if an attacker manages to get access to your network. Encrypt your data so that it cannot be read by the ransomware gang if it is stolen for use in an attempted data leak as an additional safeguard against a double extortion effort.
Protection against ransomware – how to prevent infection: Never click on unsafe links: Avoid clicking on links on untrusted websites or in spam emails. Malicious links could trigger an automated download that infects your computer if you click on them.
Avoid disclosing personal information: Do not respond if an unreliable source contacts you by phone, text, or email asking for personal information. When organizing a ransomware attack, cybercriminals may try to get personal data from you to customize their phishing messages for you. Contact the sender immediately if you have questions about the message’s validity.
Do not open suspicious email attachments: Email attachments can also deliver ransomware to your device. Any suspicious-looking extensions should not be opened. Pay special attention to the sender and verify that the address is accurate to ensure the email is reliable. Never open an attachment that requests that you execute a macro to view it. Opening an infected attachment will launch a malicious macro that allows the malware to take control of your computer.
Never use unknown USB sticks: If you are unsure of the source of any USB sticks or other storage devices, never attach them to your computer. To persuade someone to use the storage device, cybercriminals may have contaminated it and left it in a busy area.
Keep your programs and operating system up to date: You may better safeguard yourself from malware by routinely updating your operating system and software. Ensure you take advantage of the most recent security fixes when running updates. This makes it more difficult for fraudsters to exploit holes in your programs.
Use only known download sources:
- Never download software or media files from untrusted websites to reduce the chance of obtaining ransomware.
- Use reputable and trusted websites to download from. The trust seals can identify these websites.
- Ensure that “https” is used in place of “http” in the browser address bar of the page you visit. The address bar may also display a shield or lock icon to show that the page is secure.
- When downloading anything to your mobile device, use caution as well.
Depending on your device, you can put your trust in either the Google Play Store or the Apple App Store.
Use VPN services on public Wi-Fi networks: Conscious usage of public Wi-Fi networks is a practical ransomware defense strategy. Your computer is more susceptible to assaults when connected to a public Wi-Fi network. Avoid using public Wi-Fi for delicate transactions, or use a secure VPN service.
Taking Steps to Prevent Ransomware Attacks:
Educating your staff on ransomware and how it affects systems is the first step in averting a ransomware attack. Even the most reliable hardware and software cannot compensate for a negligent employee. A plan for assisting your users in recognizing and avoiding ransomware should be part of your overall strategy. Many companies have required quarterly security seminars where administrators educate staff members about possible assaults. Everything from ransomware to phishing to the rising risks from social engineering scams should be covered in your plan.
The straightforward security procedures listed below can help staff do their part to prevent these more frequent attacks.
Scan Attachments:
If email is the engine that moves it, then the attachment is the freight you unintentionally unload to introduce malware onto your system. You can check your emails for potential dangers using the scanning features available on many enterprise spam filters. Use the scanning features of your spam filter or anti-malware software before opening any email attachments.
Block Attachments:
One of the best ways to prevent ransomware at the gate is to block specific attachments. Users may be prevented from opening file extensions like.exe,.com,.bat,.js, and others that are frequently connected to malware by the system. Establishing a different server, such as one in the cloud, could be a good idea to process prohibited file types solely. This strategy could also restrict access to the legitimate data you need.
Promote Good Data Backup Habits:
Businesses find managing backups and storing data on the corporate network challenging when so many people work remotely. Encourage staff members to frequently backup their data and exercise responsibility. Employees should back up any data on a laptop’s local flash storage to the cloud or another hard drive. Employees should be sure to maintain backups offline if they keep the majority of their data on the cloud.
Encourage Stringent Cyber Hygiene:
Every employee must be reminded regularly to update their software and turn on all security features, including firewalls and anti-malware, especially those who work from home. It is a well-known staff error to neglect to apply security patches and updated software, leaving a hole that malware and ransomware can exploit.
Test Your People and Systems:
Once your network is in peak condition, it is wise to think about performing frequent testing. Testing backups, personnel, and networks for vulnerabilities are included in this because humans are frequently the weakest link in a security system. Because of this, several companies have developed plans for testing staff. This can entail distributing phony phishing emails or even hiring businesses to simulate social engineering frauds. In any event, regular testing should be a component of any security plan.
Use Email Filtering:
As a result, you receive fewer emails that could be dangerous. Businesses ought to spend money on enterprise-level solutions. To balance spam and legitimate mail filtering, they will employ strategies including allowlisting, blocklisting, and user-based email analytics.
Preach Safe Surfing:
Distribution of ransomware is not just by email, like malware in general. Visits to malicious websites, free software downloads, and even connecting infected USB sticks to your computer can all propagate this kind of virus. A computer security training course that goes over all the fundamentals of ethical web browsing can make all the difference in remaining safe.
Protection against ransomware – what companies should pay attention to:
Attacks using ransomware do not simply affect individuals. In truth, businesses are regularly the target of attacks. Small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) are being targeted by ransomware, making it a problem that doesn’t just affect big, profitable corporations. They typically have subpar security mechanisms, making them more desirable targets for attackers. The following is a list of considerations businesses looking to prevent ransomware infection should make.
Stay up-to-date with the latest operating software at all times – in the office setting. Companies that ignore this area are particularly vulnerable to ransomware attacks, as experience has shown (see, for instance, WannaCry in 2017).
Raise employee awareness – A person will be more successful at fending attacks if they know what to look for. Implement a security procedure that enables staff to determine the legitimacy of an email, attachment, or link.
Be prepared – check to see if a plan is in place for ransomware infection.
If you haven’t already, think about cloud computing. The advantage over on-premise systems is that cloud-based architectures’ weaknesses are more challenging to exploit. Additionally, you can recover earlier versions of your information using cloud storage options. This implies that by using cloud storage, you should be able to restore the original, unencrypted form of the files if they have been encrypted by ransomware.
Backups – Business-critical data should always be backed up to external devices, even in office settings. Responsibility for this crucial task should be established and communicated straightforwardly.