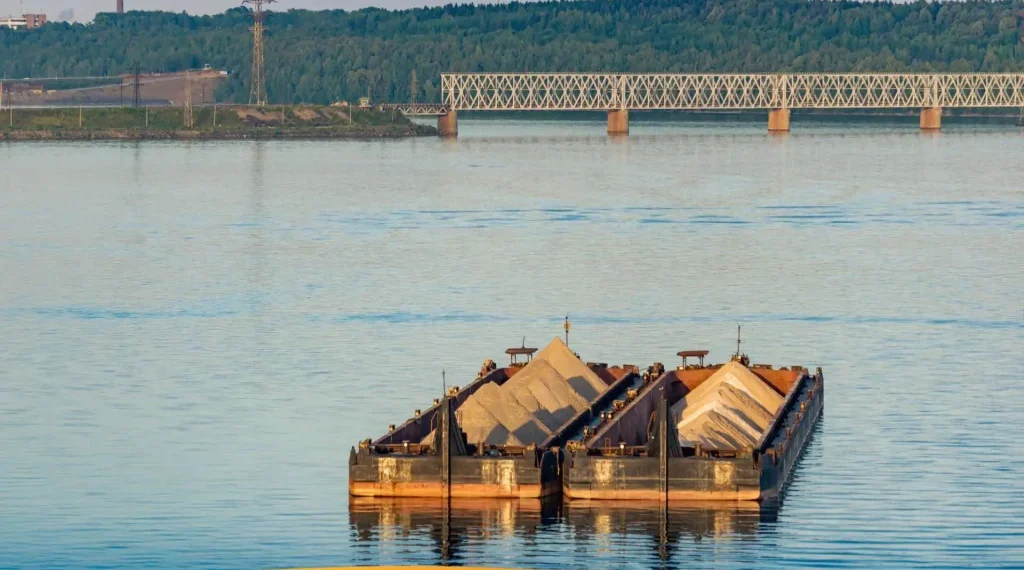
Coastal regions worldwide are increasingly vulnerable to erosion, rising sea levels, and extreme weather events. These environmental challenges threaten communities, marine ecosystems, and vital infrastructure. Dredging services, especially hydraulic dredging, are critical in mitigating these threats by protecting and restoring coastlines. Through sediment removal, waterway maintenance, and habitat restoration, dredging helps maintain the stability and resilience of coastal areas.
The growing impact of climate change has made it more necessary than ever to manage coastal environments effectively. From small coastal towns to major port cities, proactive dredging operations ensure continued safety and sustainability. This article explores the importance of dredging in coastal protection and restoration, the various techniques employed, including dredging equipment, and the long-term benefits of responsible dredging practices.
Overview of Coastal Erosion and Environmental Challenges
Coastal erosion is a natural process that continuously reshapes shorelines, yet human activities and climate change have notably influenced its acceleration. Rising sea levels, more intense storms, and coastal development efforts have intensified this erosion, resulting in the loss of beaches, wetlands, and vital marine habitats. This environmental challenge contributes to habitat destruction and increases the risks of flooding and property damage in coastal communities.
Key factors driving erosion include the persistent force of wave action, storm surges caused by extreme weather events that displace sediment, human interference through construction projects, deforestation, and pollution, as well as the degradation of natural barriers like mangroves, coral reefs, and dunes that traditionally protect the coast.
Role of Dredging in Coastal Management
Dredging is a crucial tool for coastal management, offering solutions to counteract the adverse effects of erosion and sedimentation. Dredging operations help restore beaches, deepen navigation channels, and reinforce shorelines by removing or redistributing sediments. This process ensures that ports, harbors, and waterways remain functional while preserving the ecological balance of coastal regions.
Key dredging operations in coastal management include:
- Beach Nourishment: Restoring eroded shorelines with dredged sand.
- Harbor and Channel Maintenance: Keeping waterways navigable for ships and marine transport.
- Flood Prevention: Removing excess sediment to improve water flow and drainage.
- Wetland Restoration: Rebuilding habitats to support biodiversity and enhance water quality.
Importance of Sustainable Dredging Practices
Sustainable dredging practices are essential to balance the benefits of dredging services with the need to minimize environmental impacts. These practices include eco-friendly sediment management, repurposing dredged materials for beach nourishment, wetland restoration, and land reclamation.
Additionally, efforts are made to minimize habitat disruption by scheduling activities outside sensitive breeding seasons and avoiding critical marine habitats, thereby protecting aquatic life. Using energy-efficient dredging equipment and optimized project operations further contributes to reducing the carbon footprint of dredging activities. Finally, adherence to environmental laws and regulations ensures that dredging operations are conducted responsibly and sustainably.
Understanding Dredging and Its Applications
Dredging is a process that involves excavating sediments and debris from the bottom of water bodies such as rivers, lakes, harbors, and coastal areas, with the primary goals of enhancing navigation, protecting shorelines, and supporting ecosystem restoration.
There are several techniques employed in dredging, including hydraulic dredging, which utilizes suction to remove and transport sediments through pipelines; mechanical dredging, which involves the use of heavy machinery like clamshell buckets and backhoes; cutter suction dredging, which combines mechanical cutting with suction to remove sediment efficiently; and jet-lift and air-lift dredging, which rely on water or air pressure to move sediments in confined or deep-sea environments.
The dredging equipment used in dredging services & operations varies according to the project’s requirements, ranging from cutter suction dredgers for high-precision, large-scale projects, to hopper dredgers that are designed to collect and transport sediments over long distances, as well as backhoe dredgers that are effective in confined spaces where compacted materials are present, and trailing suction hopper dredgers that are particularly suited for deep-water and offshore applications.
Coastal Protection and Dredging Services
Coastal protection and dredging services are critical in preserving shoreline integrity and supporting maritime activities. Dredging replenishes eroded beaches through beach nourishment—redistributing offshore sediment to restore coastal landscapes and prevent further erosion—and strengthens coastal defenses by deepening navigation channels and reinforcing barriers to better withstand storm surges and high tides.
Additionally, regular dredging operations are essential for maintaining navigable waterways, as they prevent sediment buildup that could obstruct vessel movement in harbors, ports, and shipping channels, thereby supporting economic activities and ensuring safe maritime operations.
Dredging for Coastal Restoration
Coastal ecosystems, such as marshlands and estuaries, rely on dredging services to restore their natural balance. Sediment removed from navigation channels can be repurposed to rebuild wetlands, create artificial reefs, and enhance fish habitats. These restoration projects improve biodiversity, water quality, and overall coastal resilience.
Advanced Techniques and Equipment
Technological advancements in dredging have significantly enhanced both operational efficiency and environmental sustainability. For instance, the integration of real-time monitoring systems enables continuous assessment of sediment levels and environmental impact throughout dredging operations. Moreover, the development of automated and remote-controlled dredgers has increased precision while reducing energy consumption, optimizing overall performance.
In addition, innovations such as geotextile containment solutions are employed to contain and stabilize dredged materials, which proves beneficial in land reclamation projects. Researchers are also exploring eco-friendly materials for dredging services, including biodegradable options, to support sediment containment further and promote habitat restoration.
Conclusion
Dredging services are essential for coastal protection and restoration, offering solutions to combat erosion, enhance navigation, and rebuild marine habitats. Dredging operations can achieve long-term environmental and economic benefits by integrating sustainable practices and advanced technologies.
Investing in research, innovation, and regulatory frameworks will be critical in ensuring the continued success of dredging projects. As climate change continues to impact coastal regions, proactive dredging efforts will be key in preserving these invaluable ecosystems for future generations. Through collaboration between governments, private sector stakeholders, and environmental organizations, we can create a sustainable approach to dredging that balances development with ecological conservation.